Linoleic Acid In Baby Formula
Linoleic acid in baby formula. In this study predigested formula preparations A and B with linoleic acid contents of 12 and 7 of energy respectively were fed before and after 1989 to infants enrolled in the evaluation and treatment protocol of the Wisconsin CF Neonatal Screening Project. At least some infant formula companies take the position that supplying alpha-linolenic acid and linoleic acid the precursors of DHA and AA respectively is sufficient since infants can convert these into DHA and AA. The fats in infant formulas are not notably different from the fats in human milk except in the content of the long-chain polyun- saturated fatty acids which are absent from formula fats and in their triglyceride structure Formulas have traditionally contained sufficient linoleic acid the w6 essential fatty acid and the growth character- istics of formula-fed infants have been excellent relative to.
In contrast infant formula marketed in the Netherlands in the early 1970s provided as much as 58 of FAs as LA resulting in very high LA contents in infant body fat and an early study in the United States of infants fed formula with 45 of FAs as LA found 2- to 3-fold higher LA contents of red blood cell phospholipid classes compared to breastfed infants. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials T Udell RA Gibson and M Makrides. Both alkene groups are cis.
Lipids 40 111 2005. Linoleic acid is an organic compound with the formula COOH CH 2 7 CHCHCH 2 CHCH CH 2 4 CH 3. Because linoleic acid is an essential nutrient it is typically provided in enteral parenteral and infant formulas where the fat content can vary depending on the specific use.
652017 7 Fat LCT. Linoleic acid vitamin K thiamine riboflavin vitamin B6 niacin pantothenic acid biotin. This is why infant formula is fortified with DHA and why pregnant and breastfeeding women are encouraged to get DHA in their diet either from a food source or a supplement.
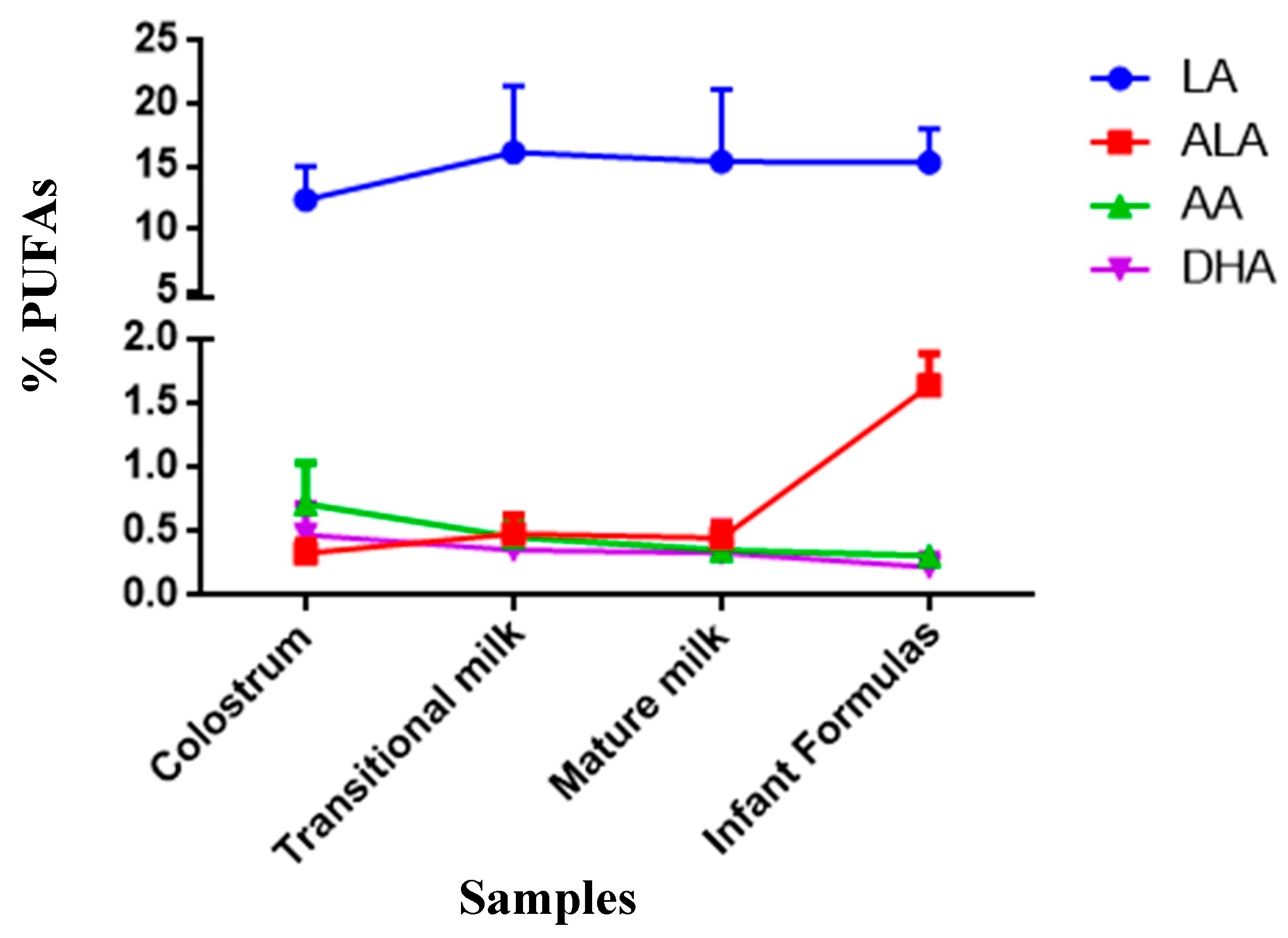
The effect of α-linolenic acid and linoleic acid on the growth and development of formula-fed infants. The boxes represent the 25th to 75th percentiles the whiskers represent the 10th to 90th percentiles and the plusses represent the 5th to 95th percentiles. Formulas for preterm infants were developed with a nutrient profile different from that of human milk and term formulas in part because of early observations that preterm infants grew better when formula human milk or banked human milk was supplemented.
1 Evidences of linoleic acid deficiency developed in young infants who received either a diet practically devoid of fat or one providing 42 of the calories as fat but extremely low in linoleic acid less than 01 of. Trans Fatty acids represented 77 of maternal total fat. Experts say both vegetable and fish omega-3s are good for your health but no one knows for sure if ALA has all the health benefits associated with DHA and EPA.
Box plots of infant weight-for-age and length-for-age z scores in breast-fed infants BF infants fed formula containing a ratio of linoleic to α-linolenic acid LAALA of 51 and infants fed formula containing an LAALA of 101. Weight LBW infants and the composition of formulas intended for feeding these infants.
DHA algae and ARA fungus MCT.
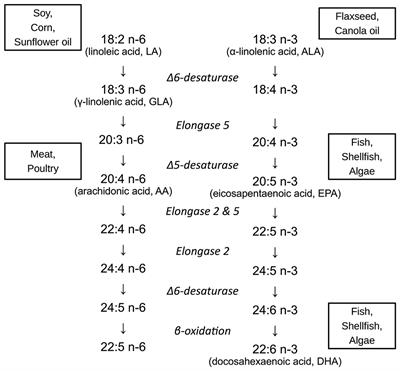
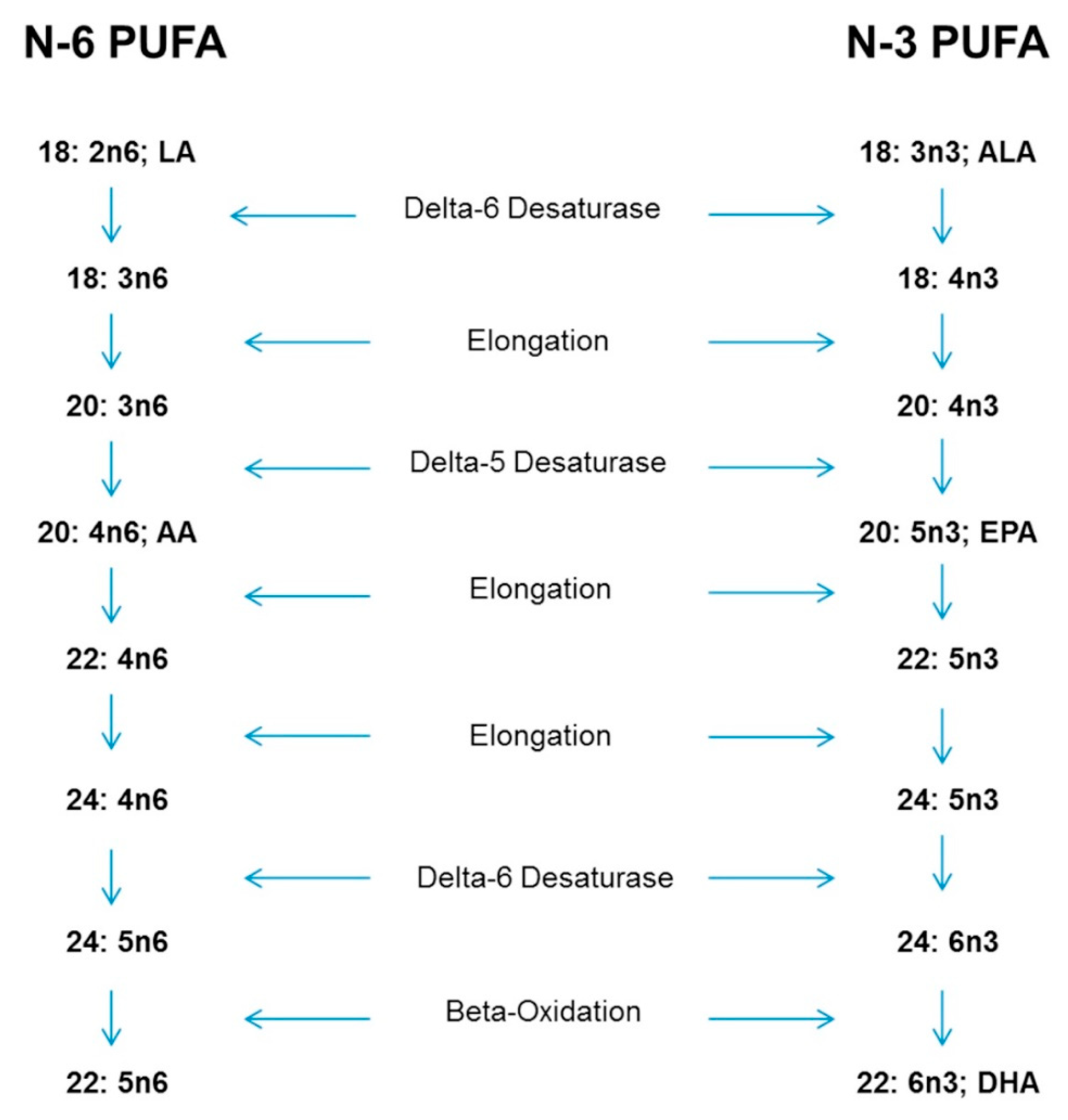
The fats in infant formulas are not notably different from the fats in human milk except in the content of the long-chain polyun- saturated fatty acids which are absent from formula fats and in their triglyceride structure Formulas have traditionally contained sufficient linoleic acid the w6 essential fatty acid and the growth character- istics of formula-fed infants have been excellent relative to. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Because linoleic acid is an essential nutrient it is typically provided in enteral parenteral and infant formulas where the fat content can vary depending on the specific use. Experts say both vegetable and fish omega-3s are good for your health but no one knows for sure if ALA has all the health benefits associated with DHA and EPA. Humans can make DHA from another fatty acid alpha linolenic acid that is now in all infant formulas but the conversion ability of newborns especially preterm babies may be unable to. Trans Fatty acids represented 77 of maternal total fat. 1 Evidences of linoleic acid deficiency developed in young infants who received either a diet practically devoid of fat or one providing 42 of the calories as fat but extremely low in linoleic acid less than 01 of. This is why infant formula is fortified with DHA and why pregnant and breastfeeding women are encouraged to get DHA in their diet either from a food source or a supplement. Humans can synthesize other omega-3 fatty acids from ALA including eicosapentaenoic acid EPA and docosahexaenoic acid DHA.
Because of the potential importance of CLA to maternal and infant health CLA concentration was quantified in human milk and infant formula. The following pertinent observations were made. Humans can make DHA from another fatty acid alpha linolenic acid that is now in all infant formulas but the conversion ability of newborns especially preterm babies may be unable to. CLA may also act as a growth promotor in the neonate. 18 carbon Linoleic acid Linolenic acid Carbohydrate. Experts say both vegetable and fish omega-3s are good for your health but no one knows for sure if ALA has all the health benefits associated with DHA and EPA. The boxes represent the 25th to 75th percentiles the whiskers represent the 10th to 90th percentiles and the plusses represent the 5th to 95th percentiles.

































Post a Comment for "Linoleic Acid In Baby Formula"